Pyoderma gangrenosum
| Pyoderma gangrenosum | |
|---|---|
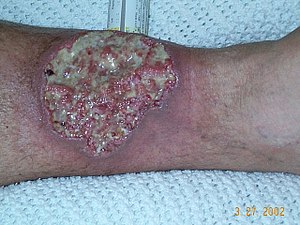 | |
| Pyoderma gangrenosum on the leg of a person with ulcerative colitis. | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | A small bump that expands into a painful ulcer and progressively grows[1][2] |
| Usual onset | 20s to 50s[1] |
| Duration | Months[2] |
| Causes | Unknown[1] |
| Risk factors | Autoimmune disorders, cancer[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms after ruling out other causes[3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Pyogenic granuloma, Sweet syndrome, sporotrichosis[3][1] |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, ciclosporin, infliximab, canakinumab[4] |
| Frequency | 1 in 100,000 per year[1] |
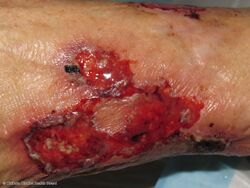
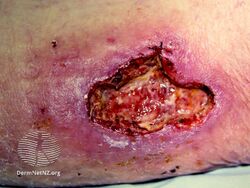
Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is a skin disease which generally begins as a small bump that expands into an ulcer which progressively grows.[1] The ulcers have well defined borders and are often painful.[1] While the legs are often affected, lesions may form anywhere.[1] It may begin in the area of a minor injury.[2]
The cause is unknown, though believed to be autoinflammatory.[1][2] It may be associated with autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), cancer including leukemia, and certain drugs and medications.[3][2] It is not infectious.[3] Diagnosis is based on symptoms after ruling out other possible causes.[3]
Treatments may include corticosteroids, ciclosporin, infliximab, or canakinumab.[4] Once healing has begun, skin grafting may be carried out.[2] Without treatment the ulcers may grow, stabilize, or gradually heal.[2] Despite treatment healing may take months and a scar may remain.[2]
About 1 per 100,000 people are newly affected per year in the United States.[1] Among those with IBD, about 2% are affected.[2] Women are more commonly affected than men.[1] Those between 20 to 50 years of age are most commonly affected.[1] The disease was first identified in 1930.[5]
Signs and symptoms
Among the presentation, for this condition are fever, joint pain and muscle inflammation[6]
-
Pyoderma gangrenosum
-
Pyoderma gangrenosum
-
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Associations
The following are conditions commonly associated with pyoderma gangrenosum:[7]
- Inflammatory bowel disease:
- Arthritides:
- Hematological disease:
- Autoinflammatory disease:
- Pyogenic sterile arthritis, and acne syndrome (PAPA syndrome)
Causes
Though the cause is not well understood, the disease is thought to be due to immune system dysfunction, and particularly improper functioning of neutrophils. In support of an immune cause, a variety of immune mediators such as interleukin (IL)-8, IL-1β, IL-6, interferon (IFN)-γ, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor alpha, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9, MMP10, and elafin have all been reported to be elevated in patients with pyoderma gangrenosum.[9]
Also in support of an immune cause is the finding that at least half of all pyoderma gangrenosum patients suffer from immune-mediated diseases.[10] For instance, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple myeloma (MM) have all been associated with pyoderma gangrenosum. It can also be part of a syndromes such as PAPA syndrome.[citation needed]
One hallmark of pyoderma gangrenosum is pathergy, which is the appearance of new lesions at sites of trauma, including surgical wounds.[11]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of PG is challenging owing to its variable presentation, clinical overlap with other conditions, association with several systemic diseases, and absence of defining histopathologic or laboratory findings. Misdiagnosis and delayed diagnosis are common. It has been shown that up to 39% of patients who initially received a diagnosis of PG have an alternative diagnosis.[12] In light of this, validated diagnostic criteria have recently been developed for ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum.[13]
Types
There are two main types of pyoderma gangrenosum:[10]
- the 'typical' ulcerative form, which occurs in the legs
- an 'atypical' form that is more superficial and occurs in the hands and other parts of the body
Other variations are:[14]
- Peristomal pyoderma gangrenosum comprises 15% of all cases of pyoderma
- Bullous pyoderma gangrenosum
- Pustular pyoderma gangrenosum[15]
- Vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum[16]
Criteria
In addition to a biopsy demonstrating a neutrophilic infiltrate, patients must have at least 4 minor criteria to meet diagnostic criteria.[13] These criteria are based on histology, history, clinical examination and treatment.[citation needed]
- Histology: Exclusion of infection (including histologically indicated stains and tissue cultures)
- Pathergy (ulcer occurring at sites of trauma, with ulcer extending past area of trauma)
- Personal history of inflammatory bowel disease or inflammatory arthritis
- History of papule, pustule, or vesicle that rapidly ulcerated
- Clinical examination (or photographic evidence) of peripheral erythema, undermining border, and tenderness at site of ulceration
- Multiple ulcerations (at least 1 occurring on an anterior lower leg)
- Cribriform or “wrinkled paper” scar(s) at sites of healed ulcers
- Decrease in ulcer size within 1 mo of initiating immunosuppressive medication(s)
Treatment
First-line therapy for disseminated or localized instances of pyoderma gangrenosum is systemic treatment by corticosteroids and ciclosporin. Topical application of clobetasol, mupirocin, and gentamicin alternated with tacrolimus can be effective.Pyoderma gangrenosum ulcers demonstrate pathergy, that is, a worsening in response to minor trauma or surgical debridement. Significant care should be taken with dressing changes to prevent potentially rapid wound growth. Many patients respond differently to different types of treatment, for example some benefit from a moist environment, so treatment should be carefully evaluated at each stage.[citation needed]
Papules that begin as small "spouts" can be treated with Dakin's solution to prevent infection and wound clusters also benefit from this disinfectant. Wet to dry applications of Dakins can defeat spread of interior infection. Heavy drainage can be offset with Coban dressings. Grafting is not recommended due to tissue necrosis.[citation needed]
If ineffective, alternative therapeutic procedures include systemic treatment with corticosteroids and mycophenolate mofetil; mycophenolate mofetil and ciclosporin; tacrolimus; thalidomide; infliximab; or plasmapheresis.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 "Pyoderma Gangrenosum". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 "Pyoderma gangrenosum". dermnetnz.org. DermNet NZ. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 14 May 2021.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Schmieder, SJ; Krishnamurthy, K (January 2021). "Pyoderma Gangrenosum". PMID 29489279.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ 4.0 4.1 Partridge AC, Bai JW, Rosen CF, Walsh SR, Gulliver WP, Fleming P (August 2018). "Effectiveness of systemic treatments for pyoderma gangrenosum: a systematic review of observational studies and clinical trials". The British Journal of Dermatology. 179 (2): 290–295. doi:10.1111/bjd.16485. PMID 29478243. S2CID 3504429.
- ↑ Ruocco E, Sangiuliano S, Gravina AG, Miranda A, Nicoletti G (September 2009). "Pyoderma gangrenosum: an updated review". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 23 (9): 1008–17. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03199.x. PMID 19470075. S2CID 29773727.
- ↑ "Pyoderma gangrenosum | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 6 May 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ↑ Brooklyn T, Dunnill G, Probert C (July 2006). "Diagnosis and treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum". BMJ. 333 (7560): 181–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7560.181. PMC 1513476. PMID 16858047.
- ↑ Tendas A, Niscola P, Barbati R, Abruzzese E, Cuppelli L, Giovannini M, et al. (May 2011). "Tattoo related pyoderma/ectyma gangrenous as presenting feature of relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia: an exceptionally rare observation". Injury. 42 (5): 546–7. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2010.08.014. PMID 20883993.
- ↑ Patel F, Fitzmaurice S, Duong C, He Y, Fergus J, Raychaudhuri SP, et al. (May 2015). "Effective strategies for the management of pyoderma gangrenosum: a comprehensive review". Acta Dermato-Venereologica. 95 (5): 525–31. doi:10.2340/00015555-2008. PMID 25387526.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Jackson JM, Callen JP (April 23, 2012). Elston DM (ed.). "Pyoderma Gangrenosum". EMedicine. Archived from the original on October 18, 2008. Retrieved November 9, 2005.
- ↑ Rashid RM (November 2008). "Seat belt pyoderma gangrenosum: minor pressure as a causative factor". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 22 (10): 1273–4. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2008.02626.x. PMID 18837131. S2CID 27476857.
- ↑ Weenig RH, Davis MD, Dahl PR, Su WP (October 2002). "Skin ulcers misdiagnosed as pyoderma gangrenosum". The New England Journal of Medicine. 347 (18): 1412–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa013383. PMID 12409543.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Maverakis E, Ma C, Shinkai K, Fiorentino D, Callen JP, Wollina U, et al. (April 2018). "Diagnostic Criteria of Ulcerative Pyoderma Gangrenosum: A Delphi Consensus of International Experts". JAMA Dermatology. 154 (4): 461–466. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5980. PMID 29450466. S2CID 4774649. Archived from the original on 2020-10-17. Retrieved 2018-02-21.
- ↑ Brooklyn T, Dunnill G, Probert C (July 2006). "Diagnosis and treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum". BMJ. 333 (7560): 181–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7560.181. PMC 1513476. PMID 16858047.
- ↑ Shankar S, Sterling JC, Rytina E (November 2003). "Pustular pyoderma gangrenosum". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 28 (6): 600–3. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2230.2003.01418.x. PMID 14616824. S2CID 11350602.
- ↑ Langan SM, Powell FC (August 2005). "Vegetative pyoderma gangrenosum: a report of two new cases and a review of the literature". International Journal of Dermatology. 44 (8): 623–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2005.02591.x. PMID 16101860. S2CID 34574262.
- ↑ Reichrath J, Bens G, Bonowitz A, Tilgen W (August 2005). "Treatment recommendations for pyoderma gangrenosum: an evidence-based review of the literature based on more than 350 patients". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 53 (2): 273–83. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2004.10.006. PMID 16021123.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 errors: missing periodical
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from September 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Articles with unsourced statements from February 2021
- Reactive neutrophilic cutaneous conditions
- Rare diseases
- Gangrene
- Necrosis
- RTT