Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
| Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Acquired epidermolysis bullosa[1] | |
 | |
| Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita | |
| Symptoms | Blisters, fragile skin, scarring, hair loss[2] |
| Usual onset | Around age 50-years[1] |
| Duration | Longterm |
| Types | Mechanobullous and non-mecahnobullous[2] |
| Causes | Antibodies to type VII collagen[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Behaviour of symptoms, DIF, autoantibodies against collagen VII[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Porphyria cutanea tarda, pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis, drug eruption[3] |
| Medication | Corticosteroids, azathioprine, dapsone[3] |
| Prognosis | Longterm, disabling[1] |
| Frequency | Rare, males=females[2] |
| Deaths | Not fatal[1] |
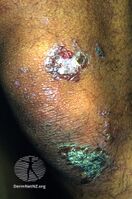
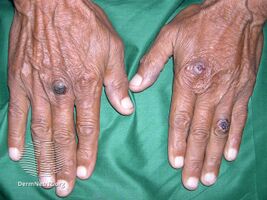
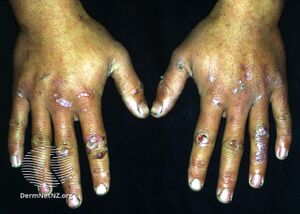
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, also known as acquired epidermolysis bullosa, is a longterm autoimmune blistering skin disease.[1] It generally presents with fragile skin that blisters and becomes red with or without trauma.[2] Marked scarring is left with thin skin, milia and nail changes.[3] It typically begins around age 50-years.[2]
It is caused by antibodies to type VII collagen within anchoring fibril structures located at the dermoepidermal junction in skin.[3] Damaged skin may become infected.[3]
Diagnosis is by observing the persistence of the condition, direct immunofluorescence, and detecting autoantibodies against type VII collagen.[2] It can appear similar to porphyria cutanea tarda, pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis, or blistering drug eruption.[3] The condition is longterm and has no cure.[1] A good response may be seen with corticosteroids, either alone or combined with azathioprine or dapsone.[3]
It is rare, with around 0.08 to 0.5 new cases per million people per year, and it affects males and females equally.[2]
Signs and symptoms
It generally presents with fragile skin that blisters and becomes red with or without trauma.[2] Marked scarring is left with thin skin, milia and nail changes.[3] It typically begins around age 50-years.[2]
-
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
-
Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
Cause
It is caused by antibodies to type VII collagen within anchoring fibril structures located at the dermoepidermal junction in skin.[3]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is by observing the persistence of the condition, direct immunofluorescence, and detecting autoantibodies against type VII collagen.[2] It can appear similar to porphyria cutanea tarda, pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis, or blistering drug eruption.[3]
Treatment
The condition is longterm and has no cure.[1] A good response may be seen with corticosteroids, either alone or combined with azathioprine or dapsone.[3]
Epidemiology
It is rare, with around 0.08 to 0.5 new cases per million people per year, and it affects males and females equally.[2]
See also
- List of cutaneous conditions
- List of target antigens in pemphigoid
- List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous conditions
- List of human leukocyte antigen alleles associated with cutaneous conditions
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Orphanet: Acquired epidermolysis bullosa". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 30 July 2017. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Kridin, Khalaf; Kneiber, Diana; Kowalski, Eric H.; Valdebran, Manuel; Amber, Kyle T. (August 2019). "Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: A comprehensive review". Autoimmunity Reviews. 18 (8): 786–795. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2019.06.007. ISSN 1873-0183. PMID 31181325. Archived from the original on 2022-03-13. Retrieved 2022-03-25.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "21. Chronic blistering dermatoses". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. p. 468-469. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2022-03-25. Retrieved 2022-03-24.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |