Erysipelas
| Erysipelas | |
|---|---|
| Other names: St. Anthony's fire,[1] Ignis sacer, holy fire[2] | |
 | |
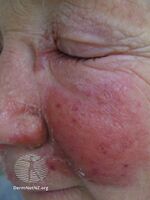
| Erysipelas of the face due to invasive Streptococcus | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Dermatology, Infectious disease[1] |
| Symptoms | Raised, well-defined, red rash, fever[3] |
| Usual onset | Rapid[3] |
| Causes | Bacterial infection[3] |
| Risk factors | Break in the skin, poor immune function, obesity, lymphoedema[2][4] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on appearance, blood test[3] |
| Differential diagnosis | Cellulitis, deep vein thrombosis, phlegmasia cerulea dolens, tenosynovitis, gout[2] |
| Treatment | Antibiotics[3] |
| Medication | Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cefalexin, cloxacillin[3] |
| Prognosis | Generally good, though may recur[5] |
| Frequency | Relatively common[3] |
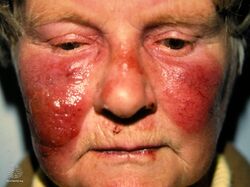
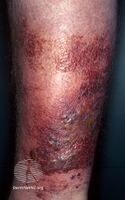
Erysipelas is an infection of part of the skin; specifically the dermis and superficial lymphatic vessels.[1] Symptoms include a painful raised, well-defined, red rash of rapid onset, and generally feeling unwell.[3] Fever and a fast pulse may be present.[3] The legs and face are most commonly involved.[5]
Most cases are caused bygroup A β-hemolytic streptococcal, but occasionally it may be caused by group C or G.[1] It may occur following break in the skin or spontaneously.[6] Other risk factors include poor immune function, obesity, and lymphoedema.[2][4] Diagnosis is generally based on its appearance.[4] A blood test may reveal a raised white cell count.[3] Swabs are usually unnecessary; though may be useful if there is pus or if not responding to usual treatment.[3] Erysipelas is a type of cellulitis which differs from other forms by being more raised with sharp borders.[4][6]
Treatment is generally with antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cefalexin, or cloxacillin) taken by mouth for 5-days; though sometimes longer.[3] NSAIDs, paracetamol (acetaminophen), and ice packs may help with discomfort.[4]
Erysipelas is relatively common.[3] The very young and old are more commonly affected.[3] The term is from Greek ἐρυσίπελας (erysípelas), meaning "red skin".[7]
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms often occur suddenly.[3] Affected individuals may develop a fever, shivering, chills, fatigue, headaches, vomiting and be generally unwell within 48 hours of the initial infection.[4][8] The red plaque enlarges rapidly and has a sharply demarcated, raised edge.[6][9] It may appear swollen, feel firm, warm and tender to touch and may have a consistency similar to orange peel.[4] Pain may be extreme.[9]
More severe infections can result in vesicles (pox or insect bite-like marks), blisters, and petechiae (small purple or red spots), with possible skin necrosis (death).[9] Lymph nodes may be swollen, and lymphedema may occur. Occasionally, a red streak extending to the lymph node can be seen.[citation needed]
The infection may occur on any part of the skin, including the face, arms, fingers, legs and toes; it tends to favour the extremities.[8] The umbilical stump and sites of lymphoedema are also common sites affected.[9]
Fat tissue and facial areas, typically around the eyes, ears, and cheeks, are most susceptible to infection.[citation needed] Repeated infection of the extremities can lead to chronic swelling (lymphoedema).[4]
Four out of five cases occur on the legs, although historically the face was a more frequent site.[10]
-
Erysipelas (ear)
-
Erysipelas face
-
Erysipelas face
-
Erysipelas leg
-
Erysipelas leg
Cause

Most cases of erysipelas are due to Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as group A β-hemolytic streptococci, less commonly by group C or G streptococci and rarely due to Staphylococcus aureus. Newborns may contract erysipelas due to Streptococcus agalactiae, also known as group B streptococcus or GBS.[9]
The infecting bacteria can enter the skin through minor trauma, human, insect or animal bites, surgical incisions, ulcers, burns and abrasions. There may be underlying eczema, athlete's foot, and it can originate from streptococci bacteria in the subject's own nasal passages or ear.[9]
The rash is due to an exotoxin, not the Streptococcus bacteria, and is found in areas where no symptoms are present; e.g., the infection may be in the nasopharynx, but the rash is found usually on the epidermis and superficial lymphatics.[citation needed]
Risk factors
Risk factors for developing the disease include [11][12][13][14]
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis, athlete’s foot, and eczema
- Excising the saphenous vein
- Immune deficiency or compromise, such as
- Diabetes
- Alcoholism
- Obesity
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- In newborns, exposure of the umbilical cord and vaccination site injury
- Issues in lymph or blood circulation
- Leg ulcers
- Lymphatic edema
- Lymphatic obstruction
- Lymphoedema
- Nasopharyngeal infection
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Pregnancy
- Previous episode(s) of erysipelas
- Toe web intertrigo
- Traumatic wounds
- Venous insufficiency or disease
Diagnosis
Erysipelas is usually diagnosed by the clinician looking at the characteristic well-demarcated rash following a history of injury or recognition of one of the risk factors.[4]
Tests, if performed, may show a high white cell count, raised CRP or positive blood culture identifying the organism.[4]
Swabs are usually unnecessary as they tend to detect normal colonising bacteria; though may be useful after being cleaned and debrided when there is pus or is not responding to usual treatment.[3]
Differential diagnosis
Erysipelas must be differentiated from herpes zoster, angioedema, contact dermatitis, erythema chronicum migrans of early Lyme disease, gout, septic arthritis, septic bursitis, vasculitis, allergic reaction to an insect bite, acute drug reaction, deep venous thrombosis and diffuse inflammatory carcinoma of the breast.[citation needed]
Erysipelas can be distinguished from cellulitis by two particular features; its raised advancing edge and its sharp borders. The redness in cellulitis is not raised and its border is relatively indistinct.[9] Bright redness of erysipelas has been described as a third differentiating feature.[15]
Erysipelas does not affect subcutaneous tissue. It does not release pus, only serum or serous fluid. Subcutaneous edema may lead the physician to misdiagnose it as cellulitis.[16][clarification needed]
Prevention
Individuals can take preventative steps to increase the chance they do not catch the disease. Properly cleaning and covering wounds is important for people battling an open wound. Effectively treating athlete's foot or eczema if they were the cause for the initial infection will decrease the chance of the infection occurring again. People with diabetes should pay attention to maintaining good foot hygiene.[11] It is also important to follow up with doctors to make sure the disease has not come back or spread. About one third of people who have had erysipelas will be infected again within three years.[12] Rigorous antibiotics may be needed in the case of recurrent bacterial skin infections.[11]
Treatment
Treatment is generally with antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, cefalexin, or cloxacillin) taken by mouth for 5-days; though sometimes longer.[3] NSAIDs, paracetamol (acetaminophen), and ice packs may help with discomfort.[4] Because of the risk of reinfection, preventative antibiotics are sometimes used after resolution of the initial condition.[4]
Prognosis
The disease prognosis includes:
- Spread of infection to other areas of body can occur through the bloodstream (bacteremia), including septic arthritis. Glomerulonephritis can follow an episode of streptococcal erysipelas or other skin infection, but not rheumatic fever.
- Recurrence of infection: Erysipelas can recur in 18–30% of cases even after antibiotic treatment. A chronic state of recurrent erysipelas infections can occur with several predisposing factors including alcoholism, diabetes, and tinea pedis (athlete's foot).[17] Another predisposing factor is chronic cutaneous edema, such as can in turn be caused by venous insufficiency or heart failure.[18]
- Lymphatic damage
- Necrotizing fasciitis, commonly known as "flesh-eating" bacterial infection, is a potentially deadly exacerbation of the infection if it spreads to deeper tissue.
Epidemiology
There is currently no validated recent data on the worldwide incidence of erysipelas.[12] From 2004-2005, UK hospitals reported 69,576 cases of cellulitis and 516 cases of Erysipelas. [12] One book stated that several studies have placed the prevalence rate between every one in 10,000 people and every 250 in 10,000 people. [11] The development of antibiotics, as well as increased sanitation standards has contributed to the decreased rate of incidence.[13] Erysipelas caused systemic illness in up to 40% of cases reported by UK hospitals and 29% of people had recurrent episodes within three years.[12] Anyone can be infected, although incidence rates are higher in infants and elderly.[13] Several studies also reported a higher incidence rate in females. [13]
History
It was historically known as St. Anthony's fire.[10]
Notable cases
- Archibald Douglas, 6th Earl of Angus, (d. 1557), Scottish nobleman active in the reigns of James V and Mary, Queen of Scots
- John of the Cross, Spanish saint and priest (d. 1591)
- Michiel de Ruyter, Dutch admiral in the Anglo-Dutch wars, contracted from injuries sustained from a cannonball. (d. 1676)
- Christina, Queen of Sweden (d. 1689)
- Anne, Queen of Great Britain and Ireland (d. 1714)
- Norborne Berkeley, baron de Botetourt, Royal Governor of Virginia (d. 1770)[19]
- Princess Amelia of the United Kingdom, daughter of George III of the United Kingdom (1783–1810)
- Grand Duchess Catherine Pavlovna of Russia, daughter of Tsar Paul I of Russia and wife of King William I of Württemberg (d. 1819)
- William Wirt, United States Attorney General and U.S. presidential candidate (d. 1834)
- Charles Lamb, English writer and essayist (d. 1834)
- Prince Augustus Frederick, Duke of Sussex sixth son and ninth child of King George III (d. 1843)
- Barbara Hofland, English children's writer and novelist (d. 1844)[20]
- Pope Gregory XVI (d. 1846)
- Mary Lyon, American women's education pioneer (d. 1849)[21]
- Marie, Dowager Duchess of Saxe-Coburg-Gotha (d. 1860)
- John Herbert White, youngest son of James S. and Ellen G. White, co-founders of the Seventh-day Adventist church (d. 1860)
- Ralph Bullock, English jockey (d. 1863)
- Frederick VII of Denmark, king of Denmark (d. 1863)[22]
- John Timon, First Roman Catholic Bishop of Buffalo, NY (d. 1867)[23]
- Nehemiah Bushnell, American attorney, railroad president, and politician (d. 1873)
- John Stuart Mill, English political philosopher (d. 1873)[24]
- Marcus Clarke, Australian journalist, poet, playwright and novelist, who wrote "For the Term of His Natural Life", died age 35 (d. 1881) [25]
- John Brown, Scottish personal servant and companion to Queen Victoria (d. 1883)[26]
- Mihai Eminescu, Romanian poet, novelist, journalist (d. 1889)
- Pat Killen, American heavyweight boxer, died at age 29 while in hiding in Chicago from police after assaulting two men (d. 1891)
- Samuel Augustus Ward, American organist, composer, teacher, businessman (d. 1903)[27]
- Johann Most, German-American anarchist politician, newspaper editor, and orator. (d. 1906)
- James Anthony Bailey, American circus ringmaster (d. 1906)[28]
- George Herbert, 5th Earl of Carnarvon (d. 1923), English aristocrat known as the financial backer of the search for and excavation of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings. His death led to the story of the Curse of Tutankhamun.
- Miller Huggins, American baseball player and manager (d. 1929)[29]
- Father Solanus Casey, American Capuchin priest declared "blessed" by the Roman Catholic Church (d. 1957)[30]
Chronic, recurrent
- Richard Wagner, opera composer, was prone to outbreaks of erysipelas throughout his adult life. He suffered notably from attacks throughout the year 1855, when he was 42.
Recovered
- Lenin suffered an infection in London, and party leadership was exercised by Martov until he recovered.[31][32][33]
- Ernest Hemingway developed an infection near his left eye after being hit with an oar. He was treated at the Casa di Cura Morgagni in Padua.[34]
Fictional
- In D. H. Lawrence's novel Sons and Lovers one of the major characters in the novel, William Morel, dies quickly from the complications of erysipelas in conjunction with pneumonia.
- In Anton Chekhov's 1892 short story "Ward No. 6", erysipelas is among the afflictions suffered by the patients committed to a poorly run mental illness facility in a small town in tsarist Russia.
- In J. G. Farrell's novel The Siege of Krishnapur the Collector, Mr. Hopkins, is afflicted during the Siege and recovers.
- In Mark Twain's Roughing It, mention is made of the disease due to the rarefied atmosphere (Chapter 43).
- In Dashiell Hammett's The Thin Man, the name is used for a pun on the word "ear" (Chapter 22).
- In Willa Cather's One of Ours, the main character, Claude, contracts the disease in "the queerest" way, after being dragged into wire by mules, and the next day continuing to work in the dust. The disease plays a key role in the novel, persuading him to marry Enid after she cares for him in recovery. (Book II, Chapter IV, p. 138).
Other animals
In other animals, erysipelas may be caused by infection with the bacterium Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. The disease may be called "diamond skin disease", which occurs especially in pigs. Heart valves and skin are affected. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae can also infect humans, but in that case the infection is known as erysipeloid.[citation needed]
Citations
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 James, William D.; Elston, Dirk; Treat, James R.; Rosenbach, Misha A.; Neuhaus, Isaac (2020). "14. Bacterial infections". Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology (13th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier. pp. 260–261. ISBN 978-0-323-54753-6. Archived from the original on 2023-12-16. Retrieved 2023-12-15.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Michael, Y; Shaukat, NM (January 2020). "Erysipelas". PMID 30335280.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) antibiotic book. World Health Organization. 2022. pp. 193–205. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 Stanway, Amy; Oakley, Amanda; Gomez, Jannet (2016). "Erysipelas | DermNet NZ". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 6 June 2020.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Stevens, Daniel L. (2022). "19. Erysipelas and cellulitis". In Jong, Elaine C.; Stevens, Dennis L. (eds.). Netter's Infectious Diseases (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier. pp. 78–80. ISBN 978-0-323-71159-3. Archived from the original on 2023-12-16. Retrieved 2023-12-15.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Wanat, Karolyn A.; Norton, Scott A. "Skin & Soft Tissue Infections - Chapter 11 - 2020 Yellow Book | Travelers' Health | CDC". wwwnc.cdc.gov. CDC. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 6 June 2020.
- ↑ Bhat M, Sriram (2019). SRB's Clinical Methods in Surgery. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers. p. 141. ISBN 978-93-5270-545-0. Archived from the original on 2020-06-06. Retrieved 2020-06-06.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 O'Brian, Gail M. (2019). "Section 1. Diseases and Disorders; Erysipelas". In Fred F. Ferri (ed.). Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2019: 5 Books in 1. Philadelphia: Elsevier. p. 523. ISBN 978-0-323-53042-2. Archived from the original on 2020-06-10. Retrieved 2020-06-06.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 Wolff, Klaus; Johnson, Richard (2009). "Part III; Diseases due to microbial agents". Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology: Sixth Edition. McGraw Hill Professional. p. 609. ISBN 978-0-07-163342-0. Archived from the original on 2020-06-08. Retrieved 2020-06-08.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Davis, Loretta S. (9 November 2019). "Erysipelas: Background, Pathophysiology and Etiology, Epidemiology". Medscape. Archived from the original on 18 December 2018. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Information, National Center for Biotechnology; Pike, U. S. National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville; MD, Bethesda; Usa, 20894 (2018-02-22). Erysipelas and cellulitis: Overview. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). Archived from the original on 2021-01-24. Retrieved 2020-12-01.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 Morris, Andrew D (2008-01-02). "Cellulitis and erysipelas". BMJ Clinical Evidence. 2008. ISSN 1752-8526. PMC 2907977. PMID 19450336.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Michael, Youstina; Shaukat, Nadia M. (2020), "Erysipelas", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30335280, archived from the original on 2021-08-28, retrieved 2020-11-13
- ↑ "Erysipelas | DermNet NZ". dermnetnz.org. Archived from the original on 2020-06-06. Retrieved 2020-11-30.
- ↑ Stevens, Dennis L.; Bryant, Amy E. (2016), Ferretti, Joseph J.; Stevens, Dennis L.; Fischetti, Vincent A. (eds.), "Impetigo, Erysipelas and Cellulitis", Streptococcus pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Manifestations, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, PMID 26866211, archived from the original on 19 September 2019, retrieved 8 June 2020
- ↑ Spelman, Denis. "Cellulitis and skin abscess: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis". UpToDate. UpToDate. Archived from the original on 17 October 2019. Retrieved 30 July 2019.
- ↑ Jorup-Rönström, Christina; Britton, S. (1987-03-01). "Recurrent erysipelas: Predisposing factors and costs of prophylaxis". Infection. 15 (2): 105–106. doi:10.1007/BF01650206. ISSN 0300-8126. PMID 3110071. S2CID 29789051.
- ↑ Nigar Kirmani; Keith F. Woeltje; Hilary Babcock (2012). The Washington Manual of Infectious Disease Subspecialty Consult. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781451113648. Page 194 Archived 2020-08-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Berkeley, Norborne, baron de Botetourt (1717–1770)". Archived from the original on 2015-02-21. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ Dennis Butts, "Hofland, Barbara (bap. 1770, d. 1844)", Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (Oxford, UK: OUP, 2004 Retrieved 20 December 2015, pay-walled Archived 28 August 2021 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Green, Elizabeth Alden (1979). Mary Lyon and Mount Holyoke. Hanover, New Hampshire: University Press of New England. p. 310. ISBN 978-0-87451-172-7.
- ↑ Møller, Jan (1994). Frederik 7. En kongeskæbne. Copenhagen: Aschehoug Dansk Forlag. p. 235. ISBN 978-87-11-22878-4.
- ↑ Castillo, Dennis (2017-04-14). "Viewpoints: Remembering Buffalo's first Catholic bishop, John Timon, 'a great and good man'". The Buffalo News. Archived from the original on 2017-04-18. Retrieved 2017-04-17.
- ↑ Capaldi, Nicholas (2004). John Stuart Mill: a biography. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. pp. 356. ISBN 978-0-521-62024-6.
- ↑ Australian Variety Theatre Archive • http://ozvta.com/practitioners-other-a-l/ Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Ridley, Jane (2013). The Heir Apparent: a life of Edward VII, the Crown Prince. New York, NY: Penguin Random House LLC. p. 287.
- ↑ America the Beautiful by Lynn Sherr
- ↑ Macy, Beth. Truevine. Little, Brown & Co, New York, 2016, page 151.
- ↑ Trachtenberg, Leo (1995). The Wonder Team: The True Story of the Incomparable 1927 New York Yankees. Bowling Green State University Popular Press. p. 151. ISBN 0-87972-677-6. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2020-07-14.
- ↑ Wollenweber, Brother Leo (2002). "Meet Solanus Casey". St. Anthony Messenger Press, Cincinnati, Ohio, page 107, ISBN 1-56955-281-9,
- ↑ Rice, Christopher (1990). Lenin: Portrait of a Professional Revolutionary. London: Cassell. ISBN 978-0304318148. pp. 77–78.
- ↑ Service, Robert (2000). Lenin: A Biography. London: Macmillan. ISBN 9780333726259. p. 150.
- ↑ Rappaport, Helen (2010). Conspirator: Lenin in Exile. New York: Basic Books. ISBN 978-0-465-01395-1 pp. 85–87.
- ↑ Hemingway, Mary Welsh (1976). How It Was. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-77265-1. p. 236.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 errors: missing periodical
- CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list
- Webarchive template wayback links
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from June 2020
- Articles with invalid date parameter in template
- Wikipedia articles needing clarification from June 2020
- Bacterial diseases
- Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions
- RTT