Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma | |
|---|---|
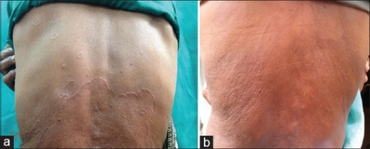 | |
| a) Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma involving back b) regressed AEGCG lesions | |
Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma (also known as "Giant cell elastophagocytosis,"[1] "Meischer's granuloma,"[2] "Miescher's granuloma of the face"[1]) is a cutaneous condition characterized histologically by a dermal infiltrate of macrophages.[1][2]: 706
Localized granuloma annulare has a tendency towards spontaneous resolution. Localized lesions have been treated with potent topical corticosteroids.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ↑ Ruby Ghadially; Akos Z Szabo; Amit Garg (January 25, 2012). "Granuloma Annulare Treatment". Medscape. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
External links
| Classification |
|---|